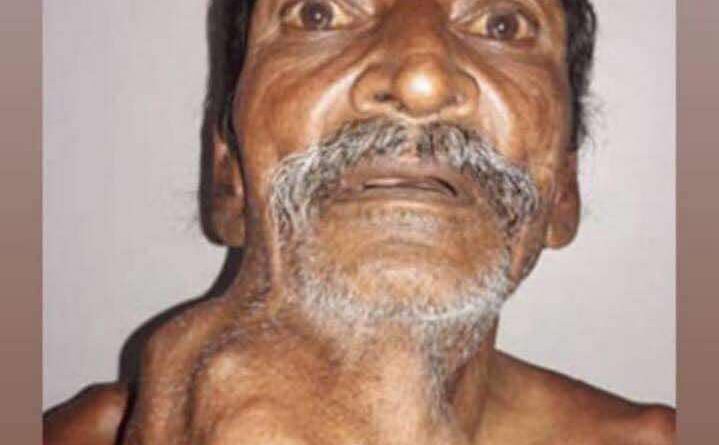
This man finally got rid of this tumor
A tumor is a mass of abnormal cells that grow and multiply uncontrollably. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Types of Tumors:
1. Benign Tumors: Non-cancerous growths that don’t invade surrounding tissues. Examples include lipomas, fibroids, and adenomas.
2. Malignant Tumors: Cancerous growths that invade and damage surrounding tissues. Examples include carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas.
3. Primary Tumors: Originate in the organ or tissue where they are found.
4. Secondary Tumors: Metastasize from a primary tumor in another part of the body.Causes and Risk Factors:
1. Genetic Mutations: Inherited or acquired genetic changes can lead to tumor development.
2. Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens, radiation, and viruses can increase tumor risk.
3. Family History: A family history of cancer or certain genetic syndromes can increase tumor risk.
4. Age: Tumor risk increases with age.
Symptoms:
1. Unintentional Weight Loss
2. Fatigue
3. Pain
4. Changes in Skin or Breasts
5. Coughing or Difficulty Swallowing
6. Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits
1. Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and PET scans help diagnose tumors.
2. Biopsy: A tissue sample is examined for cancer cells.
3. Surgery: Removing the tumor and surrounding tissue.
4. Chemotherapy: Using medications to kill cancer cells.
5. Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with a tumor, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
Would you like more information on a specific type of tumor or treatment option?